Awọn akoonu
Ni ila pẹlu iṣẹ apinfunni rẹ, Igbimọ Olootu ti MedTvoiLokony ṣe gbogbo ipa lati pese akoonu iṣoogun ti o gbẹkẹle ni atilẹyin nipasẹ imọ-jinlẹ tuntun. Àfikún àsíá “Àkóónú Ṣàyẹ̀wò” tọ́ka sí pé oníṣègùn ti ṣàyẹ̀wò àpilẹ̀kọ náà tàbí kíkọ tààràtà. Ijẹrisi-igbesẹ meji yii: oniroyin iṣoogun kan ati dokita gba wa laaye lati pese akoonu ti o ga julọ ni ila pẹlu imọ iṣoogun lọwọlọwọ.
Ifaramọ wa ni agbegbe yii ni a ti mọrírì, laarin awọn miiran, nipasẹ Ẹgbẹ ti Awọn oniroyin fun Ilera, eyiti o fun ni Igbimọ Olootu ti MedTvoiLokony pẹlu akọle ọlá ti Olukọni Nla.
Fungal otitis externa is associated with the presence of secretions in the external ear canal (EE) characteristic of a fungal infection. It appears due to injuries or water retention in the external auditory canal and in patients with diabetes, psoriasis or diabetes.
Fungal otitis externa – causes
Factors that cause fungal otitis externa can be:
- m elu Aspergillus (A.) fumigatus, A. niger, A. flavus,
- iwukara-bi olu Candida spp,
- lipophilic yeasts of the genus Malassezia.
Infection of the external ear canal can occur due to trauma, water retention in the PES, and long-term use of topical and general antibiotics. The predisposing conditions are diabetes, obesity, immune defects, psoriasis and others.
Fungal otitis externa – symptoms
Infection of the outer ear caused by fungi Aspergillus occurs as erythematous-exfoliative inflammatory lesions resembling eczema or seborrheic dermatitis, often accompanied by leakage from the ear. Sometimes there are small scab ulcers; yellow, greenish or dark patches appear on the surface of the inflamed skin, depending on the species of aspergillus.
The symptoms of fungal otitis externa include:
- irora,
- rilara titẹ ninu eti ita,
- sometimes acute hearing impairment,
- àìdá nyún.
Outer ear skin infections may be accompanied by symptoms of perchondritis. In turn, a fungal infection Candida spp. characterized by tarry, mushy discharge or erythematous skin of the external auditory canal, which may be covered with white, gray or black coating.
In both infections, the patients’ quality of life deteriorates. In the world literature there are single works on the role of Malassezia spp. In otitis externa.
Fungal otitis externa – diagnosis and treatment
In diagnostics, direct and breeding mycological tests are used. The prognosis for this ailment is generally good. Prevent recurrence by avoiding predisposing factors and treat underlying conditions for the development of fungal infections.
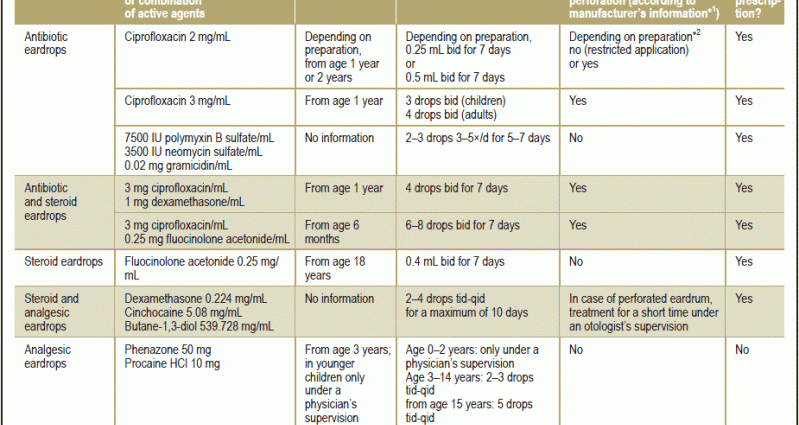
Treatment of fungal otitis externa is based on the use of clotrimazole and nystatin in drops or powder. General antifungal agents are recommended in cases of failure of topical treatment or in immunosuppressed patients.
DIG. G-51. Sprouting inflammation of the external auditory canal.
Ka tun:
- Awọn mycoses eleto – a soro alatako
- Mycosis awọ ara - awọn aami aisan, itọju
- Otitis externa - itọju, awọn aami aisan ati awọn okunfa
Akoonu ti oju opo wẹẹbu medTvoiLokony ni ipinnu lati ni ilọsiwaju, kii ṣe rọpo, olubasọrọ laarin Olumulo Oju opo wẹẹbu ati dokita wọn. Oju opo wẹẹbu naa jẹ ipinnu fun alaye ati awọn idi eto-ẹkọ nikan. Ṣaaju ki o to tẹle oye alamọja, ni pataki imọran iṣoogun, ti o wa lori oju opo wẹẹbu wa, o gbọdọ kan si dokita kan. Alakoso ko ni awọn abajade eyikeyi ti o waye lati lilo alaye ti o wa lori oju opo wẹẹbu naa.